EOF-Driven Sheath-Liquid CE-MS IF
In several publications, Dovichi and co-workers have propagated the use of a co-axial, EOF driven sheath-liquid with a borosilicate spray tube emitter for CE-MS [1-5]. The essential details are given in figures 4 and 5.
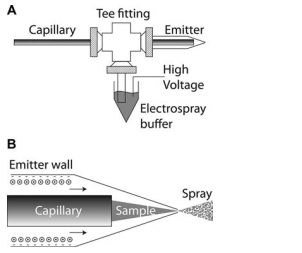
EOF-Driven Sheath Liquid CE-MS Interface according to Dovichi
The level of information (concerning details of the interface) provided in the referenced work is rather limited. A fused-silica capillary 150 µm o.d. x 10 µm i.d. is used for the CE separation. Its end is etched down to 60 µm o.d. allowing positioning close to the emitter orifice. The borosilicate emitter is home-made from a 1x0.75 mm glass tube. The emitter orifice is about 8 µm. As capillaries from borosilicate glass are known to be less robust than fused-silica, modest reliability of the emitter can be expected. On the other hand, by using 10 µm i.d. capillaries in the CE separation the exit spray acts as a true nanospray. Exceptional sensitivity is reported down to nM in solute concentration in the sample. Overall, since this design is still not commercialized, its deployment is limited to experts in the field.
![]()
[1] Sun L, Zhu G, Yan X, Champion M.M., Dovichi N.J. (2014) Proteomics 14 622-628
[2] Li Y, Wojcik R, Dovichi N.J., Champion M.M. (2012) Anal Chem 84 6116-6121
[3] Wojcik R, Li Y, Maccoss M.J., Dovichi N.J. (2012) Talanta 88 324-329
[4] Li Y, Champion M.M., Sun L, Champion P.A., Wojcik R, Dovichi N.J. (2012) Anal Chem 84 1617-1622
[5] Sun L, Zhu G, Zhao Y, Yan X, Mou S, Dovichi N.J. (2013) Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 52 13661-13664
